On backend side, unit testing is important to ensure the implementation is working as intended. While learning java for web app development (using spring), we learn that testing is needed so the application worked. Unit testing might be complicated or intimidating for starters, this will explain how unit test in java works in general.
What are Mock and Stubs
Mock is an object of class that is going to be tested.
That way, the test runner can verify some things such as the functions the object invoked during test etc.
In good practice, each class has its own test class where you create setup flow and unit tests.
On this test class, an class is tested in form of a mock object.
To fulfill it’s dependencies (class injection etc), you could inject to the mock using @InjectMocks.
Remember that the injected class is a placeholder for the class and it won’t work unless we specify it to return something.
This is where stubbing comes in.
Stubs are predetermined answers for the functions [of the injected object] called when the unit test is run.
This will ensure that the tested class behaviour in invoking functions of other class.
In java, you could use when() with many answers such as .thenReturn() or .thenThrow() to throw exception.
On more general terms, there are other definitions we use in unit testing.
- Dummy, object that passed around only to fill parameter data.
- Fake object, the object that has real implementations but has shortcuts (either in implementation or usage) it wouldn’t be used in production.
- Spies to record some information based on how they were called. (but I won’t cover this in the post)
Here’s the diagram that explain it in abstract way.
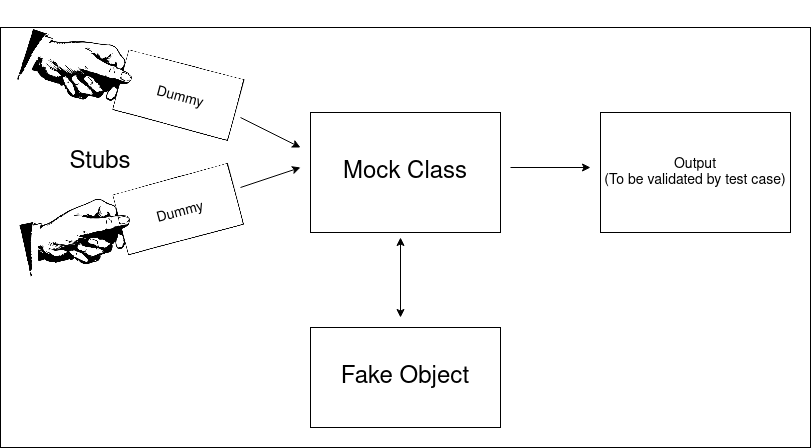
Example on MVC
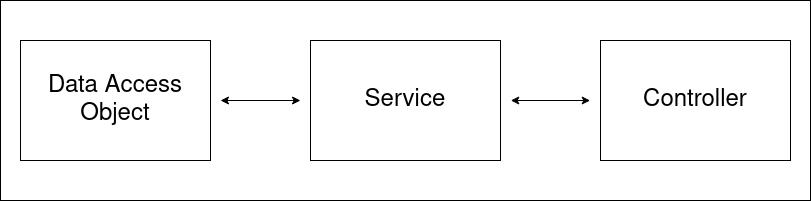
For example, we take a look on a typical API controller that has its own service and Data Access Object (DAO or Repository).
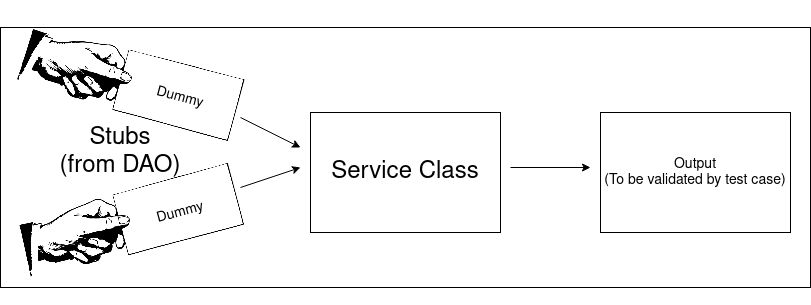
In this example, we will create test on Service Class. Each function used by the controller will be tested. Some of the functions might call a function from DAO. In that case, stubs are also used. Take note that you also need to create stub for null answers, otherwise it won’t be verified by the test runner. Here’s the diagram that describes this.
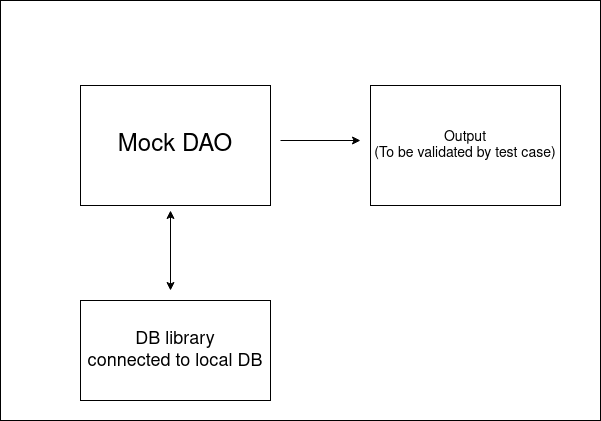
Other example involves on creating unit tests for DAO. It might be needed to verify if data is saved properly to database. Usually, we use a library to connect between application to database. It doesn’t make sense to mock it since we want to test something outside implementations. In that case, we could use fake object. For this example, we just connect the application to local database. We also need to setup the database only for unit tests and drop the data after testing.
Conclusion
Unit testing in java is not as hard as you might think. You just need to remember that the purpose of these tools is to test the behaviour of the implementation. These tools need to be learned so we could use it in easy way.